Chemicals Used As Food Preservatives
Food preservation is one of the critical issues in the food industry today. Food safety is ensured from production, through processing to storage and distribution, all the way to the consumer. The need for effective methods of food preservation has never been greater due to the increasing world population. Food preservatives are chemicals used in food products for the retardation process of spoiling caused by some microorganisms, such as bacteria, molds, and yeast, as well as to retard chemical changes compromising flavor and physical appearance.
NEET 2025: Mock Test Series | Syllabus | High Scoring Topics | PYQs
JEE Main: Study Materials | High Scoring Topics | Preparation Guide
JEE Main: Syllabus | Sample Papers | Mock Tests | PYQs
- Understanding Food Preservatives
- Types of Food Preservatives
- Real-Life Applications and Relevance
- Some Solved Examples
- Summary

These additives play a vital role in extending the shelf life of food items, hence reducing wastage toward food security. The use of food preservatives dates back several hundred years, where the early forms of preservation were processes such as salting, drying, and fermentation. However, with the advancement of food science, different types of chemical preservatives have been formulated to add more efficacy to the preservation techniques. Basically, these chemicals can be divided into two categories: natural and synthetic preservatives, each having a set of functions and applications.
Understanding Food Preservatives
Food preservatives are added to food products to help counter the action of bacteria, molds, fungi, and yeast. There are primarily two broad categories: natural and synthetic preservatives. Natural preservatives are substances derived from plants, animals, and microorganisms; examples include salt, vinegar, and some essential oils. On the other hand, synthetic preservatives are compounds manufactured from chemicals, examples of which include sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate. What is more, additives are added to retard the growth of microbes in food, prevent rancidity, and maintain the color, flavor, and texture of the food.
Food preservatives are added to increase the shelf life of products so that they remain safe and palatable longer. This is especially true for high-risk foods like meats, dairy products, and baked goods—all easily spoiled items. Preservatives contribute to enhanced food safety but also help reduce food waste at the consumption stage and earlier in the supply chain, thereby having more sustainable food systems.
Chemical substances used to protect food materials against microorganisms are called preservatives. Preservatives are classified into the following three categories depending upon the course of action:
1. Antioxidant preservatives:
These are the substances that retard the chemical reactions and breakdown of foods when they come in contact with oxygen, light, heat, and certain metals. These chemicals also stabilize some of the vitamins and amino acids present in food. Some examples of antioxidant preservatives are BHA, BHT, TBHQ, and Propyl gallate.
2. Antiripening agents:
These are used to preserve food special fruits and vegetables. These chemicals attack the enzymes that metabolize the food after harvesting. Examples of antiripening agents are citric acid, ascorbic acid, and disodium salt of ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid(EDTA).
3. Antimicrobial preservatives:
Such chemicals inhibit the growth of yeast, bacteria, or molds. Examples of such preservatives are sorbates and esters of p-hydroxybenzoic acid, sodium nitrite, sodium sulfite, calcium propionate, and sodium benzoate, etc.
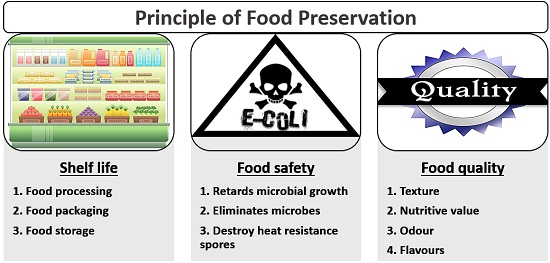
Types of Food Preservatives
Food preservatives can be classified on the basis of their function and origin.
1. Antimicrobial Agents:
Such preservatives act against the growth of bacteria and fungi. Examples are:
Sodium Benzoate: This acts against yeast and molds and is used mostly in acidic foods, for example, pickles and soft drinks.
Potassium Sorbate: Used much in milk products, baked confectionery products, and margarine for preventing spoilage.
2. Antioxidants:
These prevent oxidation, which causes rancidity and loss of flavor. Examples include:
BHA (Butylated Hydroxyanisole) and BHT (Butylated Hydroxytoluene): Added to most fats and oils in order to preserve freshness.
3. Natural Preservatives:
These are derived from plants, animals, and other natural sources, like:
Vinegar: used in pickling to create an acid environment that prevents microbial proliferation.
Salt: A traditional preservative that draws out the moisture from food and makes conditions for bacteria to grow quite unfavorable.
Their importance comes in the fact that they make the food safer and more durable, whereby people can enjoy most foods without immediate spoilage.

Real-Life Applications and Relevance
The relevance of food preservatives is not simply a matter related to the question of shelf life; it is coupled with public health and food safety. Preservatives in the food industry became a critical component in maintaining the quality for products subject to transportation and storage. For example, the use of sodium nitrite in processed meat prevents not only a detriment to the flavor but also inhibits the growth of deadly bacteria, which cause the life-threatening disease from Clostridium botulinum—botulism.
Food preservatives also play a very critical role in academic research for finding a safer and more effective method of preservation. Researchers are providing natural alternatives to synthetic preservatives due to the consumer demand for cleaner labels and healthier choices. Plant-based antimicrobials, for example, have proved to be effective preservatives for food products without bringing in all the negative health effects correlated with some synthetic food additives.
Moreover, the regulatory environment surrounding food preservatives is constantly evolving. The FDA monitors food additives for their safety quite closely; new preservatives entering the market are subjected to highly stringent safety standards. In doing so, this one will instill trust in consumers and ensure public health.
In a nutshell, preservatives are considered to be one of the inseparable parts of food production in the modern world, done to safeguard customers against food and its spoilage and thus eliminate foodborne sickness. The new consumer behaviors and increased regulatory demands have compelled the food industry to confront present and continued research into both natural and synthetic preservatives that will shape the future of food safety and quality.
Some Solved Examples
Example 1
Question:
Which of the following is not a food preservative?
1. Table salt
2. Sugar
3. Sodium Benzoate
4. Sodium Oleate
Solution:
Food preservatives prevent the spoilage of food due to microbial growth. The most commonly used preservatives include table salt, sugar, vegetable oils, sodium benzoate, etc.
Sodium Oleate is not a preservative. It is a soap.
Hence, the answer is the option (4).
Example 2
Question:
Which of the following is not an anti-ripening agent?
1. Citric Acid
2. Ascorbic Acid
3. Disodium salt of ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA)
4. Sodium Sulphite
Solution:
Examples of anti-ripening agents are citric acid, ascorbic acid, and the disodium salt of ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA).
Sodium Sulphite is an anti-microbial preservative.
Hence, the answer is the option (4).
Example 3
Question:
Which of the following is used as an antioxidant for foodstuffs?
1. Saccharin
2. Sodium Stearate
3. Alitame
4. Sodium Sulphite
Solution:
Antioxidants retard the action of oxygen on the food, helping its preservation. Sodium Sulphite
Therefore, the answer is option (4).
Example 4
Question:
The class of compounds known by the name of ______ which cures infection caused by microorganisms.
1. Antimicrobials
2. Narcotic Analysis
3. Antiseptic
4. Analgesics
Solution:
Antimicrobials are chemicals that cure infections caused by microorganisms.
Hence, the answer is the option (1).
Summary
This paper discussed the requirement of preservatives in increasing the shelf life and making the food more secure. We defined food preservatives and their different types, such as antimicrobial agents, antioxidants, and natural preservatives. The functions of such additives in high-risk foods, especially with reference to the health status of the population and food security, have been identified.
Also Read
20 Oct'24 05:41 PM
20 Oct'24 05:38 PM
20 Oct'24 05:16 PM
19 Oct'24 12:31 PM
19 Oct'24 12:26 PM
19 Oct'24 12:19 PM
19 Oct'24 12:15 PM
19 Oct'24 12:13 PM
19 Oct'24 11:58 AM


