Phosphorus: Definition, Properties, Formula and Examples
Phosphorus takes centre stage in many major biological and industrial functions. It's the element, aside from explaining plant growth, that is one of the simple building blocks for the molecule containing genetic material in all living things, otherwise known as DNA . Phosphorus enters our lives through its presence in the tips of matches and in those detergents that wash our clothes.
NEET 2025: Mock Test Series | Syllabus | High Scoring Topics | PYQs
JEE Main: Study Materials | High Scoring Topics | Preparation Guide
JEE Main: Syllabus | Sample Papers | Mock Tests | PYQs
- Understanding Phosphorus
- Different Forms of Phosphorus
- White Phosphorus
- Red Phosphorus
- Phosphates
- Importance and Uses
- Some Solved Examples
- Summary

Understanding Phosphorus
Phosphorus is an element symbolized in the periodic table by "P" with atomic number 15. It naturally occurs in an enhanced amount through the way phosphates rocks.
Phosphorus is key to life since its presence is a determinant factor given that it holds a reservoir of DNA, RNA, and ATP, that is, the energy currency linked inside cells. It has had several allotropic forms in existence, although the two most popular allotropes are white phosphorus and red phosphorus. Of the two, white phosphorus is highly reactive with spontaneous ignition in the air, while red phosphorus is more stable and less hazardous.
Different Forms of Phosphorus
Phosphorus is found in many allotropic forms, the important ones being white, red and black.
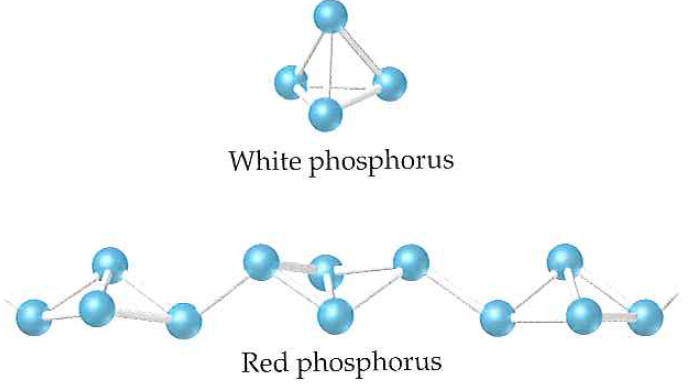
White phosphorus is a translucent white waxy solid. It is poisonous, insoluble in water but soluble in carbon disulphide and glows in the dark (chemiluminescence). It dissolves in boiling NaOH solution in an inert atmosphere giving PH3.

White phosphorus is less stable and therefore, more reactive than the other solid phases under normal conditions because of angular strain in the P4 molecule where the angles are only 60°. It readily catches fire in the air to give dense white fumes of P4O10.
Red phosphorus is obtained by heating white phosphorus at 573K in an inert atmosphere for several days. When red phosphorus is heated under high pressure, a series of phases of black phosphorus is formed. Red phosphorus possesses an iron-grey lustre. It is odourless, non-poisonous and insoluble in water as well as in carbon disulphide. Chemically, red phosphorus is much less reactive than white phosphorus. It does not glow in the dark.

It is polymeric, consisting of chains of P4 tetrahedra linked together in the manner shown in the figure given above.
Black phosphorus has two forms α-black phosphorus and β-black phosphorus. α-Black phosphorus is formed when red phosphorus is heated in a sealed tube at 803K. It can be sublimed in air and has opaque monoclinic or rhombohedral crystals. It does not oxidise in the air. β-Black phosphorus is prepared by heating white phosphorus at 473 K under high pressure. It does not burn in air upto 673 K.
White Phosphorus
White phosphorus is a waxy, white, fairly transparent solid, and it glows weakly in the dark when air oxygen is present. It is a very toxic and highly reactive substance. Primarily, it is used militarily, relating to incendiary weapons and smoke bombs.
Red Phosphorus
Red phosphorus is much more stable and less reactive than white phosphorus. It is used in the manufacture of fertilizers, pyrotechnics, and flame retardants for various materials. White phosphorus spontaneously changes to red phosphorus when heated or exposed to light.
Phosphates
The phosphates are a class of compounds including phosphorus and oxygen. They are vastly applied in agriculture as fertilizers in increasing soil fertility. This also happens in detergents and food additives, among others, other than their main application, which is in the manufacture of the main raw material in the sodas called phosphoric acid.
Importance and Uses
Biological Importance
Phosphorus is the other most biologically vital element. It is part and parcel of the precursors to nucleic acids —bases in DNA and RNA. Speaking genuinely, phosphorus is part of the structure of ATP, a cellular molecule that stores and transfers energy. Such a chemical element is very fundamental in the formation of bones and teeth, whereby calcium phosphate is deposited to make up bone minerals.
Industrial Uses
More industrially, it is further used in the manufacture of steel and phosphor bronze alloys. The compounds have a host of uses in the production of pesticides, detergents, and flame retardants. The semiconductor industry uses phosphorous by doping silicon wafers since it facilitates the process of raising their electric properties.
Environmental Impact
Such runoff from agricultural fields of P into high algal growth water bodies can cause eutrophication, deplete oxygen, and destroy aquatic life. Hence, the use of phosphate and controlling pollution are serious factors that contribute to sustainability in the long term.
Recommended topic video on(phosphorous)
Some Solved Examples
Example 1
Question:
The number of pentagons in C60 are x and the trigons (triangles) in white phosphorus are y, then write answer xy.
(if x=30, y= 1 then answer xy will be 301).
1)203
2) (correct)124
3)123
4)204
Solution:
Number of pentagons in ( C60 = 12
Number of trigons in white phosphorus = 4
Therefore, ( xy = 12 times 4 = 48 )
So, the answer is 124.
Therefore, Option (2) is correct.
Example 2
Question:
Red phosphorus is prepared by -
1) Heating of white phosphorus at 300 K
2) Heating of white phosphorus at 573 K
3) Heating of black phosphorus at 300 K
4) Heating of black phosphorus at 573 K
Solution:
Red phosphorus is prepared by heating white phosphorus in an inert atmosphere at a temperature of 573 K.
Therefore, Option (2) is correct.
Example 3
Question:
The hybridisation of phosphorus in red phosphorus is -
1) sp
2) sp2
3) sp3
4) sp3d
Solution:
Red phosphorus exists as chains of ( P4 ) tetrahedra linked together through covalent bonds. The hybridization of phosphorus in red phosphorus is ( sp3).
Therefore, Option (3) is correct.
Summary
Phosphorus has been an astoundingly important element biologically, industrially, and environmentally. It has applications in agriculture and industries in a way that sustainable life could hardly do without; the critical building blocks of DNA, transferring energy between cells. Therefore, understanding the characteristics and uses of this element easily leads to new advancements in technological sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The major application of phosphorus is devoted to agriculture as the content of fertilizers. It promotes the development of roots, flowers, seeds, and fruits in plants. The phosphates in the fertilizers raise soil fertility and enlarge the agrarian yield.
This excess phosphorus released through agricultural runoff undergoes eutrophication in different water bodies, stimulating algal growth that consumes available oxygen in water and drastically deteriorates the condition of fish and other aquatic life. Management of phosphorus is, therefore, inevitable to prevent environmental degradation.
Allotropic forms of the element are mainly noted to be white and red since others are less common. White phosphorus is highly reactive and highly toxic, whereas the red form is much more stable. It is also used in safety matches and as a flame retardant. Others form phosphates, greatly applied in agriculture processes and industry.
It is one of the essential elements in the body since it forms the backbone for DNA, RNA, and ATP, which have major biological functions both in maintaining information and in the energy transfer within the cell. Moreover, in the form of calcium phosphate, it forms bones and teeth.
Phosphorus is used in steels and alloys of all types. It is also used in producing pesticides, detergents, and fire retardants. First and foremost, however, it is to the semiconductor industry that phosphorus is of key importance because it is used in doping silicon wafers for desired electrical properties.
Also Read
05 Mar'25 04:40 PM
19 Feb'25 07:01 PM
19 Feb'25 06:59 PM
19 Feb'25 06:57 PM
19 Feb'25 06:53 PM
18 Oct'24 09:35 AM
18 Oct'24 09:28 AM
17 Oct'24 11:41 PM
17 Oct'24 11:21 PM
17 Oct'24 11:16 PM

