Silicones
Silicones belong to the class of synthetic Polymers that have woven themselves. They are conspicuous in many industries and everyday products. They are artificial polymers with a rather uncommon chemical structure based on silicon and oxygen atoms in a chain-like alternating pattern. This gives rise to some remarkable properties for silicones, most importantly the flexibility, durability, resistance to high and low temperatures
NEET 2025: Mock Test Series | Syllabus | High Scoring Topics | PYQs
JEE Main: Study Materials | High Scoring Topics | Preparation Guide
JEE Main: Syllabus | Sample Papers | Mock Tests | PYQs
- Silicones
- Types of Silicone and Applications
- Some Solved Examples
- Summary
Silicones
Silicones are a type of synthetic polymer having a main chain containing an alternating arrangement of silicon and oxygen atoms in a siloxane structure. This difference in structure, with most other organic polymers having carbon in the backbone, is responsible for different behavior from one another. The general formula for silicones is (R2SiO)x, where R refers to attached organic groups to the silicon atoms. In doing so, it gives silicones the ability to range within a wide spectrum of physical forms—from liquids to solids—for specific applications.
Polymerization of silicones principally starts with the reaction of silica with methyl chloride to obtain dimethyldichlorosilane. After that, this is further hydrolyzed into silanol, which undergoes polymerization to yield the silicone polymer. These silicones have low toxicity and are highly thermally stable against moisture; hence, they find very broad application fields in industries related to healthcare, automobiles, and consumer goods.
They are a group of organosilicon polymers, which have (R2SiO) as a repeating unit. The starting materials for the manufacture of silicones are alkyl or aryl-substituted silicon chlorides, RnSiCl(4–n), where R is the alkyl or aryl group. When methyl chloride reacts with silicon in the presence of copper as a catalyst at temperature 573K various types of methyl-substituted chlorosilane of formula MeSiCl3, Me2SiCl2, Me3SiCl with small amount of Me4Si are formed. Hydrolysis of dimethyl-dichlorosilane, (CH3)2SiCl2 followed by condensation polymerization yields straight-chain polymers.
2CH3Cl+Si→570 KCu powder (CH3)2SiCl2→−2HCl+2H2O→(CH3)2Si(OH)2
The chain length of the polymer can be controlled by adding (CH3)3SiCl which blocks the ends as shown below.

Silicones being surrounded by non-polar alkyl groups are water-repelling in nature. They have in general high thermal stability, high dielectric strength, and resistance to oxidation and chemicals. They have wide applications. They are used as sealants, greases, electrical insulators, and for waterproofing of fabrics. Being biocompatible they are also used in surgical and cosmetic plants.
![]()
Types of Silicone and Applications
There are many kinds of silicones, which are differentiated based on physical state and intended use. The main ones are silicone fluids, elastomers, gels, and resins.
1. Fluids: Low-viscosity liquids used in applications such as lubricants, hydraulic fluids, and water repellants. When used in personal-care applications, they improve in feel and performance.
2. Silicone Elastomers: Very good flexibility and durability open an immense scope of application in most medical devices, automotive, and domestic appliances like bakeware. Good heat and cold resistance make it perfect for high-performance applications.
3. Silicone Gels: Semi-solid materials with huge stakes in smooth and breathable applications in cosmetics and personal care, letting the skin breathe.
4. Silicone Resins: Such materials are rigid, resistant to abrasion, and find basic uses in coatings, adhesives, and sealants. They provide good weather resistance and are mostly applied in the building and automobile industries.
The versatility of silicones makes them tailor-made for various applications across sectors, from health to electronics, through construction, down to personal care. For instance, in the automotive sector, silicone adhesives play a very major role in the manufacturing process in terms of sealing and bonding of automobile parts. There are also silicone coatings that improve the durability of surfaces under hostile environmental conditions.
Recommended topic video on (silicones)
Some Solved Examples
Example 1:
Correct statements among a to d regarding silicones are :
(a) They are polymers with hydrophobic character
(b) They are biocompatible
(c) In general, they have high thermal stability and low dielectric strength.
(d) Usually, they are resistant to oxidation and used as greases
1)(a), (b), (c) and (d)
2)(a), (b) and (c) only
3)(a) and (b) only
4) (correct)(a), (b) and (d) only
Solution
Silicones
Polymeric organo-silicon compounds having (R2SiO)n general formula where R= alkyl or aryl groups
They have high thermal stability but have high dielectric strength.
Hence, the answer is the option (4).
Example 2 :
Among the following substituted silanes the one which will give rise to cross-linked silicone polymer on hydrolysis is
1)R3SiCl
2)R4Si
3) (correct)RSiCl3
4)R2SiCl2
Solution
As we have learned,
In Silicones,
the chain propagating agent is R2SiCl2
the chain terminating agent is R3SiCl
the chain cross-linking agent is RSiCl3
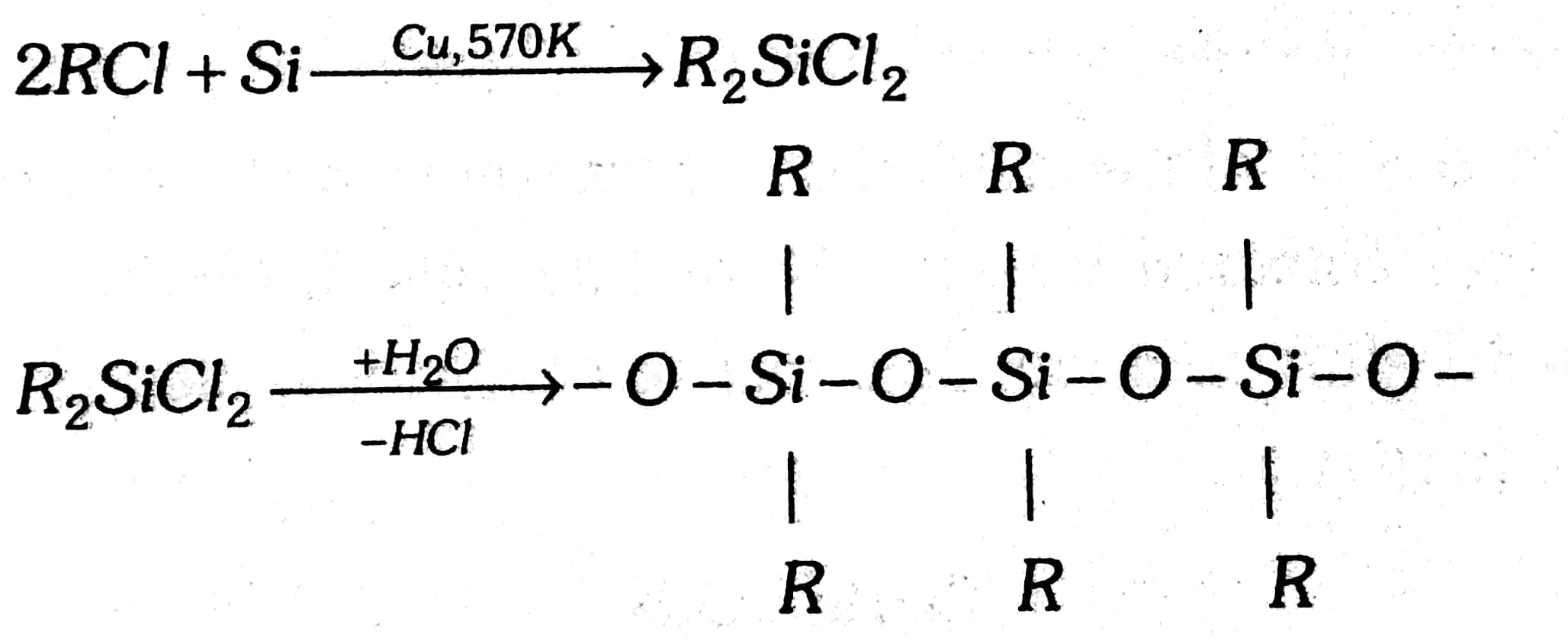

Therefore, option (3) is correct.
Example 3:
Silicones are –
1)Water-repelling
2)Thermally stable
3)Have high dielectric constant
4) (correct) All of the above
Solution
As we have learned,
Silicones are Water-repelling, thermally stable, and have a high dielectric constant.
Hence, the answer is the option (4).
Summary
The importance of silicones reaches from the industrial to daily, mostly overlooked, uses: from medical devices and construction materials down to personal care. They form one of the most critical fields in medicine and technology because of their biocompatibility, flexibility, and resistance to factors of the environment. Their durability and adaptiveness help them retain relevance in consumer goods.
Also Read
19 Feb'25 06:55 PM
19 Feb'25 06:49 PM
19 Feb'25 06:45 PM
19 Feb'25 06:41 PM
19 Feb'25 05:03 PM
17 Oct'24 12:24 PM
11 Oct'24 10:25 AM
11 Oct'24 12:09 AM
05 Oct'24 12:20 AM

