Electric Current - Definition, Types, Applications, FAQs
Electricity is the flow of charge through a material in an electric current, usually expressed in amperes. In current electricity behaviour, its movements are mostly a result of the movement of electrons through a conductor such as a wire. A pressure difference, which can be likened to an electric pressure, initiates this flow as it forces electrons along a path with low resistance. The existence of electrical devices that help in facilitating life atoms’ motion and operation of current technological advancements depends largely on this movement of electrons. In this article we will discuss the concept of electric current, it is a keystone to different technologies and applications.
This Story also Contains
- What is an Electric Current?
- Types of Current
- Effects of Electric Current
- Solved Examples Based on Electric Current

What is an Electric Current?
Electric current is defined as the rate of flow of electric charge through any cross-section.
i.e If a charge flows through an area for time $\Delta t$ then average electric current through the area is defined as-
$\bar{i}=\frac{\Delta Q}{\Delta t}$
The instantaneous current at any time t is given by
$ i=\lim _{\Delta t \rightarrow 0} \frac{\Delta Q}{\Delta t}=\frac{d Q}{d t}$
If the flow is uniform then the Current
$ I=\frac{Q}{t} $
If a current I flows through an area for time t then, the total charge flowing is
$Q=\int I d t$
Till now we have studied the current now will study about it's direction.
Properties of Electric Current
- An electron flow in the circuit is what causes current.
- By adding resistance to the circuit, it is possible to regulate the flow of electric current.
- Amperes are used to measure electric current (A). One coulomb of charge can be moved in one second at a rate of one ampere.
- In a circuit, electrical current flows from higher electric potential to lower potential (from the positive terminal to the negative terminal), often referred to as the traditional direction of current flow.
Conventional Current flow Vs Electron Flow
As Current is the rate of flow of charge, Charge can be +ve or -Ve.
The direction of positive charge flow is considered the conventional direction of current. The direction opposite to the direction of the flow of negative charge is considered the conventional direction of the current.


Current flows through a circuit only if the circuit is closed.
For a Closed-circuit
-
Conventional current: Positive terminal to negative terminal
-
Electron current: Negative terminal to Positive terminal
Calculating Current in Different Situations
-
When the charge is performing translatory motion
-
$\text { If } n \text { particles each having charge } q \text { pass a given area in time } t$
$i=\frac{n q}{t}$
-
When the charge is performing a rotatory motion
If a point charge q is moving in a circle of radius r With Velocity V (frequency $\nu$, angular speed $\omega$ and time period T ). Then,
$ i=\frac{q}{t} \Rightarrow \frac{q}{T}=q \nu=\frac{q V}{2 \pi r}=\frac{q w}{2 \pi}$
Related Topics
Types of Current
-
Alternating current

-
Magnitude and direction both vary with time.
-
Shows a heating effect only.
-
Its symbol

-
Direct current

-
No change in magnitude and direction with time.
-
Shows the heating effect, chemical effect, and magnetic effect of current.
Current Independent of Area
Current does not change with change in cross-sectional area
Here $i_1=i_2=i_3$

Effects of Electric Current
Electricity has three main effects:
-
Chemical effect
Heating Effect
When an electric current flows through a conductor, some of the electrical energy is converted into heat energy. This is called the heating effect of electric current. The heat produced depends on three factors: the square of the current $\left(I^2\right)$, the resistance of the conductor $(R)$, and the time for which current flows $(t)$. This is expressed by Joule's law of heating:
$
H=I^2 R t
$
Magnetic Effect
The movement of electrons is all that constitutes an electric current, and as is well known, while charges are resting, they produce an electric field, and when charges are moving, they produce a magnetic field. The presence of a magnetic field produced by the electric current causes the needle to deflect when a metallic sheet is inserted into a wire with electricity flowing through it. Electromagnets, which are created with the aid of electric current, are one of the most common uses of the magnetic effect of electric current. A conductor or wire-carrying current creates a magnetic field that is perpendicular to the direction of the field.
Chemical Effect
A solution ionizes or separates into ions, whenever an electric current flows through it. This is due to the fact that when an electric current flows through the solution, a reaction occurs. The developments and associated effects can be seen in the solution, depending on the type of electrodes used and the composition of the solution.
Solved Examples Based on Electric Current
Example 1: One billion electrons pass from A to B in 1 ms. What is the direction and magnitude of the current?
1) 1.6 A
2) 0.8 mA
3) 0.16$\mu$A
4) 1.6 mA
Solution:
Translatory motion of charge
i=n q A
wherein
If $n$ particles charge $q$ pass per second per unit area, the current associated with a cross-section area $A$ is:
$i=\frac{N e}{t}=\frac{\left(10^9\right)\left(1.6 * 10^{-19} \mathrm{C}\right)}{10^{-3}}=1.6 * 10^{-7} \mathrm{~A} $
i = 0.16 m A.
The current flows from B to A.
Hence, the answer is the option (3).
Example 2: The average value of a sinusoidal A.C. current over one cycle is:
1) Positive
2) Negative
3) Zero
4) Can be positive negative or zero.
Solution:
Alternating current
magnitude and direction both vary with time
wherein
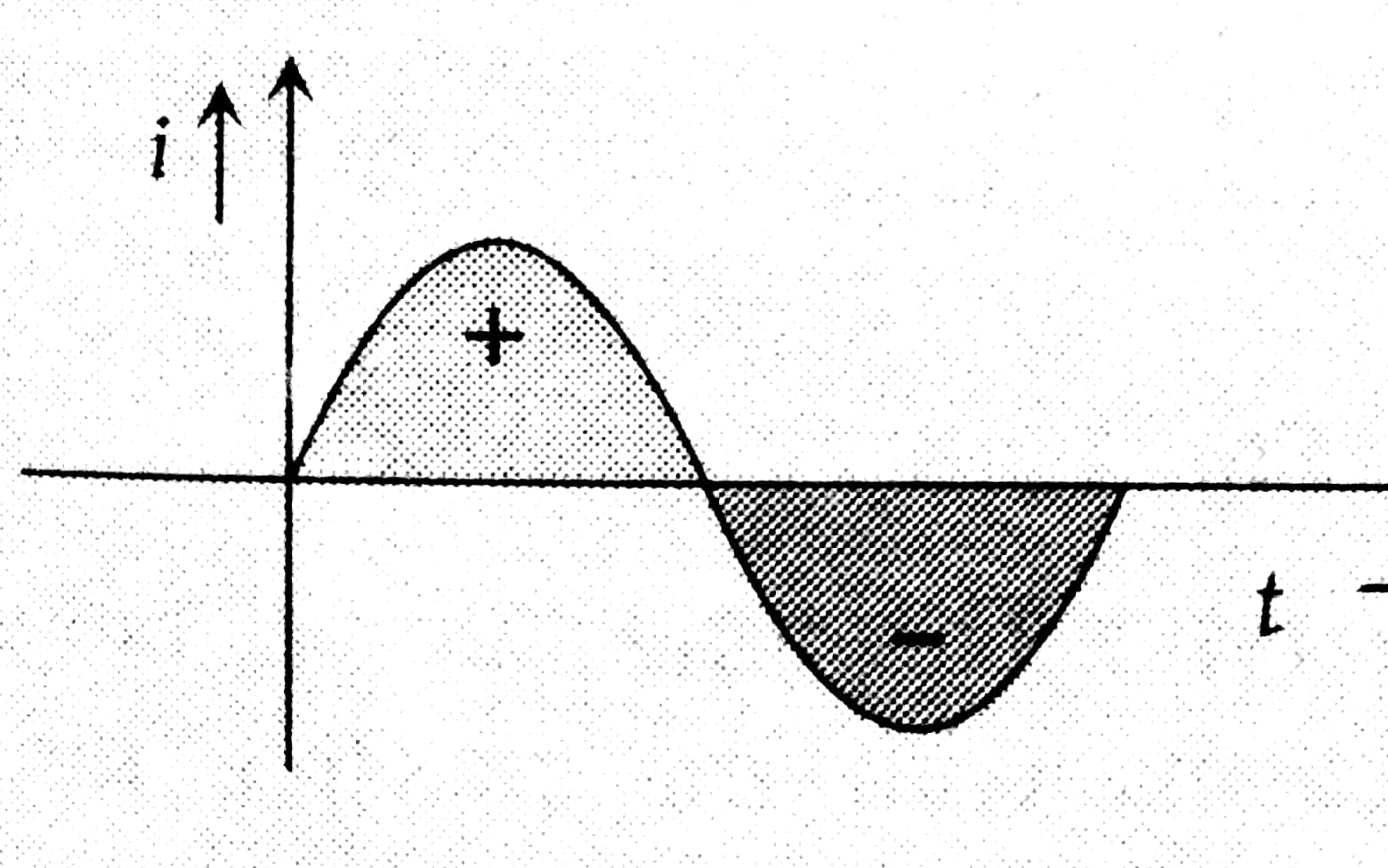
The average of sinusoidal A.C. current over one cycle is zero.
Hence, the answer is option (3).
Example 3: Alternating current can
1) produce a heating effect
2) Be used for Charging of battery
3) can be used for electrolysis
4) All of the above
Solution:
Alternating current
Shows a heating effect only.
A.C. current cannot be used for electrolysis or battery charging as its average value is zero.
Hence, the answer is the option (1).
Example 4: Direct current has
1) Both magnitude and direction constant
2) only magnitude constant
3) only direction constant
4) None of the above
Solution:
Direct current
No change in magnitude and direction with time.
wherein
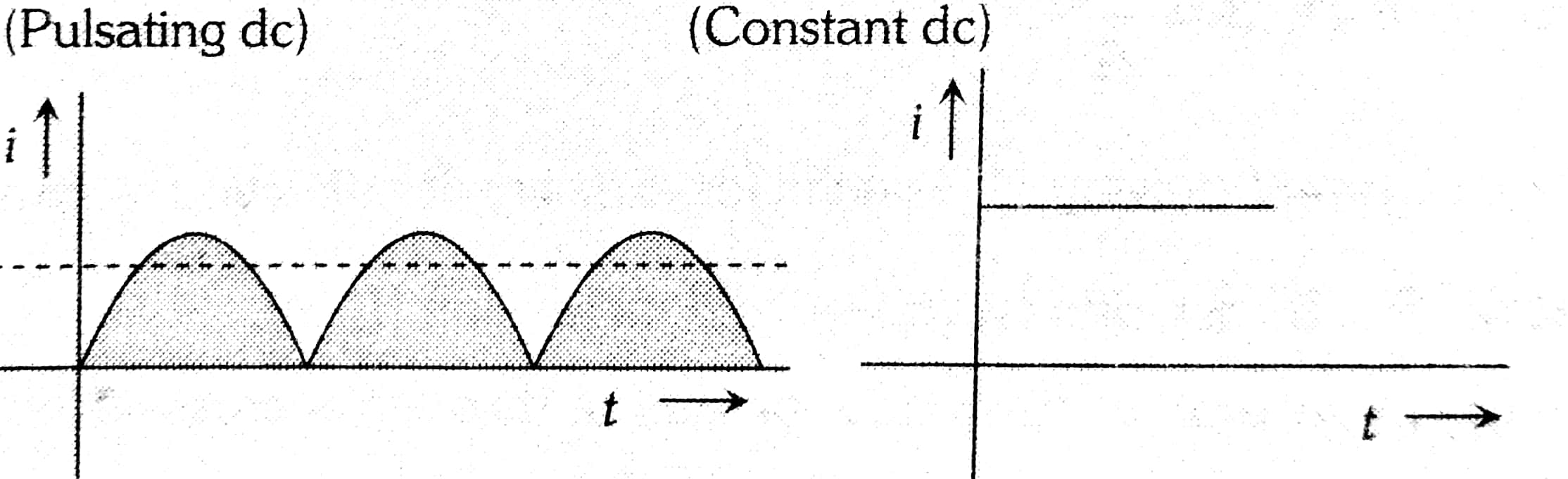
Direct current has their direction constant. i.e. it cannot reverse its direction.
Hence, the answer is option (3).
Example 5: Which of the following effects can be shown by both direct current and alternating current?
1) Magnetic effect
2) heating effect
3) Chemical effect
4) Charging of battery
Solution:
Alternating current Shows a heating effect only.
But direct current Shows the heating effect, chemical effect and magnetic effect of current.
Hence, the answer is the option (2).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The term electric current simply means the rate at which the electrical charge or electrons flow inside a material. Mathematically Electric current is written as I=dQ/dt where dQ is the change in electrical charge which passes in a given period of time dt. The SI unit of electric current is known as Ampere which is denoted by A.
Electricity refers to the electrical energy and this form of energy is due to the electric current. where Electric current is the rate at which electrical charge electrons flow in a given region of space. Hence, Electricity consists of electric current and electric current consists of electrical charge electrons.
In an electrical circuit, the direction of electric current is always in a direction opposite to that of flow of electrons inside the conductor. The direction of electric current in a circuit is always represented by the direction from the positive terminal of a battery to the negative terminal of the battery.
Since our human body is a good conductor of electricity and due to this if electric current of high intensity passes through our human body, following are the major effects of electric current on human body.
Our nervous system may experience high electrical shock when electric current passes through the human body.
High intensity electric current while passing through the human body may instantly damage brain function, heart operations.
Even a small amount of electric current produces an instant little electrical shock to our whole body.
So, it’s always advised to follow all precautions while working with electricity for any purpose.
Electric current is calculated by using the formula I=Q/t here, we have Q=8C and t=2s on putting the values we get, I=8/2=4A A is denoted for ampere, Ampere is the SI unit of electric current.