Electric Potential
Electric potential is like the driving force behind electricity. It determines how electric charges behave and move through wires and circuits. Think of it as the push or energy that enables electricity to flow from one point to another. This push, measured in joules per coulomb, explains why batteries can power devices, lights turn on when you flip a switch, and appliances work when plugged in. Understanding electric potential helps us comprehend how electricity operates in our everyday lives, influencing everything from powering gadgets to lighting up our homes.
JEE Main/NEET 2027: Physics Important Formulas for Class 10
NEET 2025: Mock Test Series | Syllabus | High Scoring Topics | PYQs
JEE Main: Study Materials | High Scoring Topics | Preparation Guide
JEE Main: Syllabus | Sample Papers | Mock Tests | PYQs
- Electric Potential
- Solved Example Based On Electric Potential
- Summary

In this article, we will cover the concept of Electric Potential. This concept is in the class 12th electrostatic chapter. It is not only essential for board exams but also for competitive exams like the JEE Main, NEET, and other entrance exams such as SRMJEE, BITSAT, WBJEE, BCECE and more. Over the last ten years of the JEE Main exam (from 2013 to 2023), a total of six questions have been asked on this concept. And for NEET two questions were asked from this concept. It is a very important topic for understanding the electrostatic chapter and many questions are asked about this concept.
Electric Potential
In an Electric field Electric potential V at a point, P is defined as work done per unit charge in changing the position of test charge from some reference point to the given point.
Note-usually reference point is taken as infinity and potential at infinity is taken as Zero.
We know that
Since
where
- It is a scalar quantity.
SI Unit
1 volt
- Dimension -
Electric Potential at a Distance 'r'
If the Electric field is produced by a point charge q then
Using
Electric Potential difference
In the Electric field, the work done to move a unit charge from one position to the other is known as the Electric Potential difference.
If the point charge Q is producing the field
Points A and B are shown in the figure.

Superposition of Electric potential
Statement- Total electric potential at a given point in space due to all the charges placed around it is the scalar or algebraic addition of electric potential due to individual charges at that point.
i.e
The net Electric potential at a given point due to different point masses (Q1,Q2,Q3…) can be calculated by doing a scalar sum of their individual Electric potential.

- Electric Potential due to Continuous charge distribution
- Graphical representation
As we move on the line joining two charges then the variation of Potential with distance is given below.
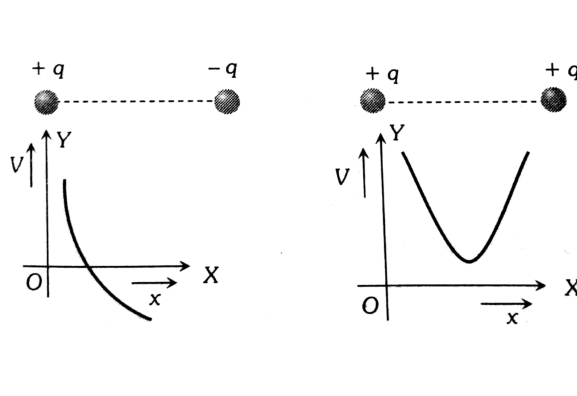
Zero Potential Due to a System of a Two-Point Charge
1. For internal point
(It is assumed that
Let at

If both charges are like then the resultant potential is not zero at any finite point.
2. For external point
Let P, V be zero

For More Information On Electric Potential, Watch The Below Video:
Solved Example Based On Electric Potential
Example 1: Two thin wire rings each having a radius R are placed at a distance d apart with their axes coinciding. The charges on the two rings are +Q and -Q The potential difference between the centers of the two rings is
1) zero
2)
3)
4)
Solution:
As we learnt in
Electric Potential -
- wherein
w - work done
q0 - unit charge.

Hence, the answer is option (4).
Example 2: The figure shows three points
1)
2)
3)
4)
Solution:
As we have learned,
Equipotential Surface -
All Points have the same Potential.
Electric lines of force flow from higher potential to lower potential so,
VA=VB>VC
Hence, the answer is option (2).
Example 3: Four charges
1)
2)
3)
4) none of these
Solution:
As we learned
Potential of a System of Charge -
At centre
E=0
and V = 0 due to symmetry structure.
Example 4: A charge Q is uniformly distributed over a long rod AB of length L, as shown in the figure. The electric potential at the point O lying at a distance L from the end A is :

1)
2)
3)
4)
Solution:
As we discussed in
Potential Difference -
Charge on the element
Potential at 0
Hence, the answer is option (1).
Example 5: Two points
1) -9.60 x 10-17 J
2) 9.60 x 10-17 J
3) -2.24 x 10-16 J
4) 2.24 x 10-16 J
Solution:
As we learnt in
Potential Difference -
Hence, the answer is option (4).
Summary
Electric potential, otherwise known to most as voltage, is the potential energy available at a particular point of an electric field per unit of charge. It is measured in volts, thereby showing the work per unit charge that is required to move a charge between two points. High electric potential simply means that there is more potential energy 'available' to move charges—it is referred to as the electromotive force, able to drive current through a circuit. Knowledge of electric potential is very important in the design of electrical systems, ranging from simple circuits to large-scale power grids, and also for the safe and efficient use of electrical devices.
Also Read
29 Nov'24 01:09 AM
14 Nov'24 06:11 PM
25 Sep'24 06:30 PM
25 Sep'24 01:34 PM
25 Sep'24 12:59 PM
25 Sep'24 12:06 PM
24 Sep'24 06:12 PM
24 Sep'24 04:45 PM
24 Sep'24 11:32 AM
13 Aug'24 11:07 AM

