Magnetic Field Lines
Magnetic field lines are a fundamental concept in physics, representing the direction and strength of magnetic fields around magnets and electric currents. These lines, although invisible to the naked eye, play a crucial role in various real-life applications. For instance, they guide the operation of electric motors, which are essential for countless devices from household appliances to industrial machinery. Additionally, magnetic field lines are integral to the functioning of compasses, which have historically been used for navigation and continue to be vital in modern technology. In this article, we will discuss important points regarding magnetism, magnetic field lines and solved examples for better understanding.
JEE Main/NEET 2027: Physics Important Formulas for Class 10
NEET 2025: Mock Test Series | Syllabus | High Scoring Topics | PYQs
JEE Main: Study Materials | High Scoring Topics | Preparation Guide
JEE Main: Syllabus | Sample Papers | Mock Tests | PYQs
- Important Points Regarding Magnetism
- Magnetic Field
- Solved Examples Based on Magnetic Field Lines

Important Points Regarding Magnetism
- The earth behaves as a magnet with the magnetic field lines pointing from the geographic south to the north.
- When a bar magnet is freely suspended, it points in the north-south direction. The tip which points to the geographic north is called the north pole and the tip which points to the geographic south is called the south pole of the magnet.
- There is a repulsive force when like poles of two magnets are brought close together and there is an attractive force when unlike poles of two magnets are brought close together.
- The north and south poles cannot be separated by splitting the magnet into two parts i.e. If a magnet is broken into a number of pieces each piece becomes a magnet.
- It is possible to make magnets out of iron and its alloys.
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field is a region in space where magnetic forces are exerted, surrounding magnets and electric currents. Though invisible, its effects are evident in numerous aspects of our daily lives. For example, the Earth itself generates a magnetic field that plays a crucial role in navigation, guiding compasses and protecting our planet from harmful solar radiation. Space around a magnetic Pole or magnet or current-carrying wire within which its effect can be experienced.
Magnetic Field Lines
Magnetic field lines are a conceptual tool used to represent the direction and strength of a magnetic field around a magnet or electric current. These lines, though not physically present, provide a way to visualize how magnetic forces radiate from the poles of a magnet and interact with their surroundings. The magnetic field line is not real. The magnetic field lines are a visual and intuitive realization of the magnetic field.
Properties of Magnetic Field Lines
- The magnetic field lines of a magnet form continuous closed loops. Outside the magnet, magnetic field lines start from the north pole and end at the south pole, whereas inside the magnet its direction is from the south pole to the north pole.
- The tangent to the magnetic field line at a given point represents the direction of the net magnetic field (
For the below figure, The tangent to the magnetic field line at point P represents the direction of the net magnetic field (

- The larger the number of magnetic field lines crossing per unit area, the stronger the magnitude of the magnetic field (
- The two magnetic field lines do not intersect at any point.
Recommended Topic Video
Solved Examples Based on Magnetic Field Lines
Example 1: Three identical bars A, B and C are made of different magnetic materials. When kept in a uniform magnetic field, the field lines around them look as follows :

Make the correspondence of these bars with their material being diamagnetic (D), ferromagnetic (F) and paramagnetic (P) :
1)
2)
3)
4)
Solution:
Diamagnetic Substance
Relative permeability of diamagnetic substance.
Diamagnetic materials are repelled in an external magnetic field. Bar B represents diamagnetic materials.
Hence, the answer is the option (2).
Example 2: Two similar bar magnets P and Q, each of magnetic moment M, are taken, if P is cut along its axial line and Q is cut along its equatorial line, all the four peces obatained have
1) Equal pole strength
2) Magnetic moment M/4
3) Magnetic moment M/2
4) Magnetic Moment M
Solution:
Monopole Concept
If a magnet is broken into a number of pieces each piece becomes a magnet.
wherein
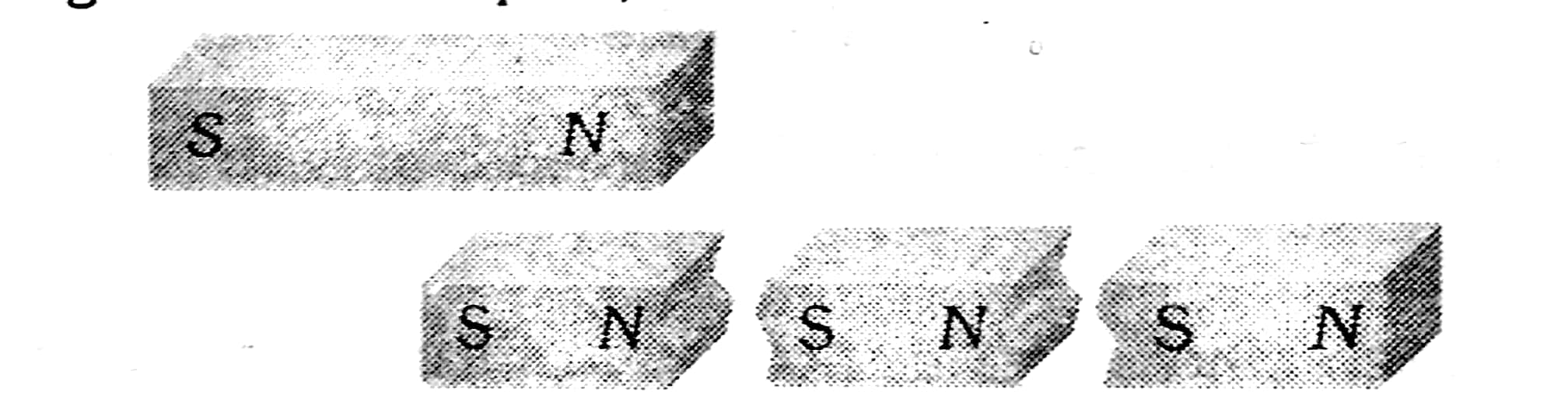
If pole strength, magnetic moment and length of each part are m', M' and L' respectively then
Hence, the answer is the option (3).
Example 3: The magnetic lines of force inside a bar magnet
1) are from northpole to southpole of the magnet
2) do not exist
3) depend upon the area of the cross section of the bar magnet
4) are from southpole to northpole of the magnet.
Solution:
Magnetic field
Space around a magnetic Pole or magnet or current-carrying wire within which its effect can be experienced.
wherein
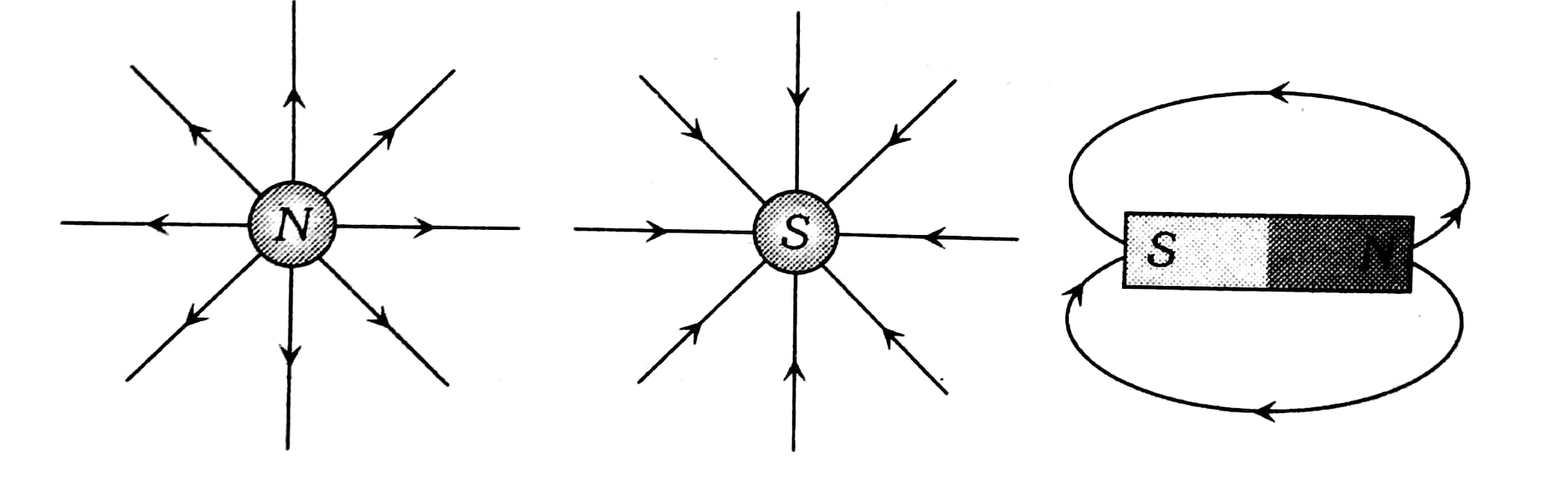
The magnetic lines of force inside a bar magnet are from the south pole to the north pole of a magnet.
Hence, the answer is the option (4).
Example 4: The lines of force due to the earth's horizontal component of the magnetic field are:
1) Parallel Straight lines
2) Concentric circles
3) Elliptical
4) Parabolic
Solution:
Magnetic field lines
The magnetic field line is not real. It is only a concept developed as an aid to visualize the effect of a field. Parallel & Straight lines are made by Earth's magnetic Horizontal.
Hence, the answer is the option (1).
Summary
Magnetic field lines provide a visual representation of magnetic fields, crucial for understanding the behavior of magnets and electric currents. They form continuous loops from the north to south pole outside a magnet and the reverse inside. These lines aid in designing and optimizing technologies like electric motors and MRI machines, highlighting the intersection of theoretical physics and practical applications. Understanding the properties of magnetic field lines helps in solving various problems related to magnetism and its effects.

