Heat Transfer Convection - Definition, Examples, Types, FAQs
Convection is a process of heat transfer that takes place in liquids and gases. In this process, heat is carried from one place to another by the actual movement of fluid particles. When a part of a fluid is heated, it becomes lighter and rises, while the cooler and heavier part sinks. This continuous movement helps in transferring heat. Convection plays an important role in our daily life. We feel warm air from a room heater and cool air from a ceiling fan because of convection. It is also seen when water boils on a gas stove. Large-scale convection currents in air and water are responsible for winds, ocean currents, and changes in weather and climate. Thus, convection helps in spreading heat effectively in nature.
This Story also Contains
- What is Convection Heat Transfer?
- Heat Transfer By Convection
- Solved Examples Based On Heat Transfer By Convection

What is Convection Heat Transfer?
Convection is the process of heat transfer through a fluid (liquid or gas) caused by the movement of the fluid itself. It occurs when warmer, less dense portions of the fluid rise, and cooler, denser portions sink, creating a circulation pattern. This transfer of heat can happen naturally due to temperature differences (natural convection) or be forced by external means, such as a fan or pump (forced convection).
Examples of Convection
- A radiator is a device that emits warm air from the top and draws cooler air in from the bottom. A steaming cup of hot tea - When you drink a cup of hot tea, the steam you observe signals that heat is being transported into the air. Ice melts because heat from the air is transferred to the ice.
- When water boils, the molecules that are denser sink to the bottom, and the molecules that are less dense rise, resulting in a circular motion of the molecules, which heats the water.
- Warm water goes towards the poles as it approaches the equator, while cooler water moves towards the equator.
- Warm-blooded animals use convection to circulate their blood, which helps to regulate their body temperature.
Also, read
- NCERT Solutions for All Subjects
- NCERT Notes For All Subjects
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for All Subjects
Heat Transfer By Convection
Convection is the heat transfer due to the bulk movement of molecules within fluids such as gases and liquids. Convection is of two types -
1. Natural Convection
The main cause of this is the difference of densities at two places and is a consequence of gravity because on account of gravity, the hot light particles rise up (density becomes less) and cold heavy particles (density becomes high) try setting down. It mostly occurs on heating a liquid/fluid.

2. Forced Convection
If a fluid is forced(by means of a fan or draught or any external means) to move to take up heat from a hot body then the convection process is called forced convection. In this case, Newton's law of cooling holds good. According to which rate of loss of heat from a hot body due to moving fluid is directly proportional to the surface area of the body and the excess temperature of the body over its surroundings.

Application of Convection
- Convection currents in the water pipes cool car engines. Water is an excellent conductor of heat away from the engine and into the radiator.
- Convection currents are what cause land and sea winds.
- Convection currents are rising air over land that glider pilots employ to maintain their gliders in the air.
- Air conditioners are placed toward the room's ceiling to allow for the formation of convection currents. Cool, dry air is blown into the room by the air conditioner. Cool air sinks because it is denser. Warm air rises because of is less dense. The air circulated, and the temperature of the air fell to the ideal level over time.
Convection Examples
Sea breeze: This phenomenon occurs during the day. The sun heats up both the sea surface and land. As the sea has a greater heating capacity, it absorbs much of the sun's energy but gets warmed up much slower than the land. As a result, the temperature above the land rises and heats the air in the atmosphere above it. Warm air is less dense, and hence, it expands, creating a low-pressure area over the land near the coast. Meanwhile, there is relatively high pressure over the sea. The difference in air pressure causes the air to flow from sea to land. The sudden gush of wind felt due to this is known as the sea breeze.
Land Breeze: This phenomenon occurs during the night when the situation reverses. As the sun sets, the land and sea start cooling down. The land quickly loses heat when compared to water due to the differences in heat capacity. Consequently, the temperature of the sea is relatively higher, which creates low air pressure there. This sets up a flow of cool breeze offshore, known as the land breeze.
What Does the Term "Thermal Convection" Mean?
Heat convection is the physical movement of a fluid (liquid, gas, or plasma) from one area to another to transfer thermal energy. In liquids and gases, heat convection is frequently the primary mechanism of energy transmission. Convection is one of three primary ways of heat transport, along with conduction and radiation.
Recommended Topic Video
Solved Examples Based On Heat Transfer By Convection
Example 1: It is hotter for the same distance over the top of fire than it is on the side of it, mainly because
1) Air conducts heat upwards
2) Heat is radiated upwards
3) Conversion takes more heat upward.
4) Conversion, conduction, and radiation all contribute significantly to transferring heat upwards.
Solution:
Convection: Mode of transfer of heat through migration of material particles of the medium.
Convection significantly transfers heat upwards. The top of a fire is hotter than its sides because hot air rises, creating a column of intense heat directly above the flames, while the heat is more dispersed on the sides.
Hence, the answer is the option (2).
Example 2: The layer of the atmosphere is heated through
1) Convection
2) Conduction
3) Radiation
4) 2 & 3 both
Solution:
Natural Convection
This arises due to the difference in densities at the two places.
wherein
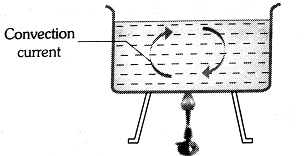
The heating of the atmosphere is mainly because of natural convection.
Hence, the answer is the option (1).
Example 3: Heating of a room using a blower is an example of
1) Conduction
2) Natural convection
3) Forced convection
4) Radiation
Solution:
Forced Convection
If a fluid is forced to move to take up heat from a hot body.
wherein
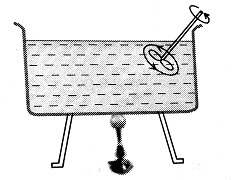
So, heat transfer with the help of a blower is an example of heat transfer through forced convection.
Hence, the answer is option (3).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
In solids, this is the most common mechanism of heat transport. Convection: If the medium is a fluid (i.e., anything that can flow), the medium particles can carry thermal energy and deliver it across. This mode has a bulk flow of medium particles.
Temperature variations between air parcels or heat transfer at surfaces cause natural convection (i.e. surface-to-air temperature difference). Natural convection becomes the sole way for air to mix inside confined spaces when forced convection is unavailable.
Yes, they are same.
Ice melting is an excellent illustration of convection. Because heat transfers from the air to the ice, it melts.
Convection is a type of thermal energy transmission that occurs in gases or liquids (whereas conduction occurs most often in solids) and is dependent on variations in heat.
